Owning an exotic pet can be a rewarding experience that affords family members the opportunity to learn about new and different species. Caring for a rabbit or lizard, however, is much different than walking a dog. Here are tips on caring for some common exotic pets.

Rabbits
If you’re looking for a cuddly exotic pet, a rabbit may be the way to go. Rabbits make great pets because they are quiet, gentle, and can even be trained to use a litter box.
Housing
Although a pet rabbit will enjoy hopping about and socializing, a cage is a necessity when you cannot directly supervise her. Rabbits are notorious for gnawing on furniture, carpet, shoes, and electrical cords, so a safe place of refuge is critical for her safety—and your belongings! Find a cage large enough for your bunny to stretch out fully and stand up on her haunches. Avoid wire flooring, as it will be hard on your rabbit’s feet and can cause chronic inflammation and infection.
Diet
Rabbits are natural herbivores, which means they consume a plant-based diet. Feed a ration of rabbit pellets daily, and keep her supplied with a constant source of hay to graze on. You can also mix in small amounts of fresh vegetables as a treat. Healthy options include:
- Cabbage
- Cauliflower leaves
- Broccoli leaves
- Kale
- Turnip greens
- Mustard greens
Health concerns
Common ailments of pet rabbits include:
- Overgrown teeth — Rabbits have front teeth that grow continuously. If they don’t align properly, the teeth will not wear down as they should and may need to be professionally trimmed.
- Respiratory infections — A bacterial respiratory infection called “snuffles” is the most common infectious illness of rabbits. Affected bunnies exhibit cold-like symptoms and must be treated with antibiotics.
- Back injuries — Rabbits have a high muscle-to-bone ratio, predisposing them to back trauma or fracture if they struggle against restraint or suddenly jump from their owner’s arms.

Birds
Birds are fun, low-maintenance pets that love to interact with their owners. Some species can even be taught to talk and perform tricks.
Housing
Birds should spend most of their time in a cage that is roomy enough for them to move about freely. Several perches should be included, along with toys that will provide mental stimulation. Your bird’s cage should be placed in an area that allows him to see and interact with family members during the day, however, birds need a dark, quiet place to get 10–12 hours of rest each night.
Diet
It is a common misconception that birds should be fed a seed-based diet. Diets containing mostly seeds are nutrient-deficient and can cause a number of diseases. Feed a commercially pelleted diet appropriate for the species of bird you choose with small amounts of fruits and vegetables added for variety. Good choices include:
- Papaya
- Mango
- Berries
- Broccoli
- Squash
- String beans
- Sweet potato
Health concerns
Frequent health issues of our feathered friends:
- Feather plucking — Birds that are bored or anxious tend to obsessively pull out their feathers. Since they are highly intelligent animals, birds need plenty of opportunities for mental stimulation. Provide enrichment items, such as toys, cardboard boxes, paper towel rolls, and those that encourage foraging for food.
- Egg binding — Female birds of some species will lay eggs in their cage. Low calcium levels can cause an egg to become stuck in the uterus, causing a life-threatening emergency.
- Chlamydiosis — Caused by the bacteria Chlamydophila psittaci, avian chlamydiosis is the leading cause of respiratory infections in pet birds.
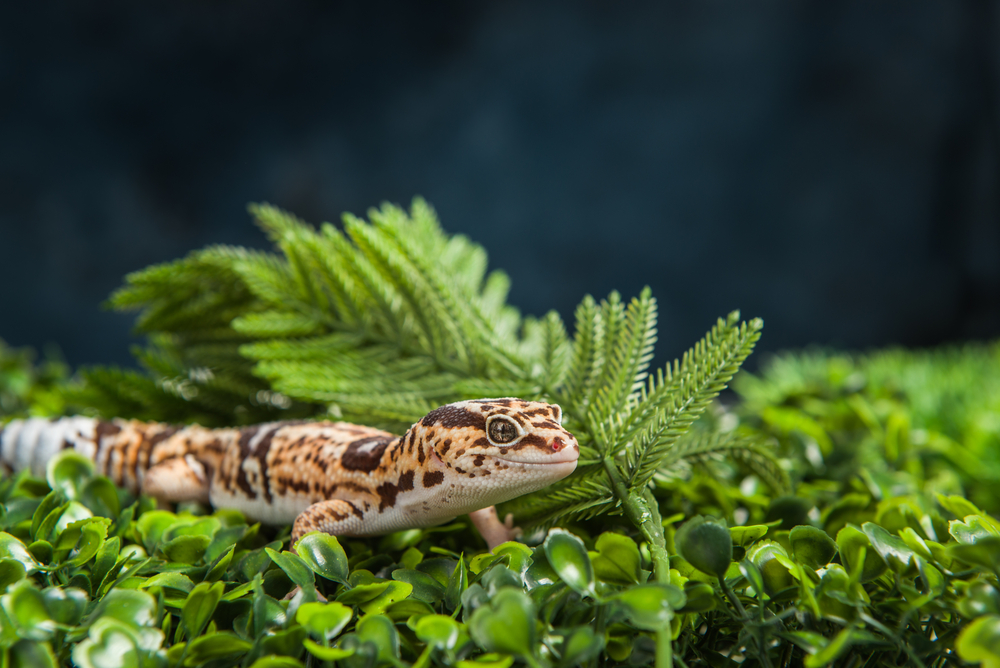

Reptiles
Snakes and lizards are increasingly popular pets. The diversity of species available can have different housing and nutritional needs; be sure to do your research so you know how to properly care for the species you choose.
Housing
Choose a cage that will allow your scaly pet plenty of room to move around. Most reptiles also appreciate a shelter or hiding place. Because reptiles are cold-blooded, most will need a heat source. Safe heating sources should be placed outside of the cage, on one side, so your reptile can choose a comfortable temperature. Some reptiles also require a UVB light in order to make adequate amounts of vitamin D to absorb dietary calcium.
Diet
Different species of lizards have different dietary requirements. Lizard species can be herbivorous (plant eaters), insectivorous (insect eaters), carnivorous (meat eaters), or omnivorous (mixed diet). It is important to research the type of food your lizard needs for proper health. Many lizard species also need a calcium supplement added to the diet.
All snakes are carnivorous and are typically fed dead rodents. Although it may seem more natural to feed live prey, bites from rodents can cause life-threatening wounds.
Health concerns
Most diseases of reptiles are linked to improper husbandry and lack of adequate nutrition.
- Vitamin deficiency — Proper diet, UV lighting, environmental temperature, and vitamin supplementation (for some species) are needed for adequate nutrition. Because it can be difficult to get these factors just right, vitamin deficiencies are the most common type of health problem to affect pet reptiles.
- Shedding difficulty (dysecdysis) — As reptiles grow, they regularly shed their skin. Lack of environmental humidity and malnutrition can cause parts of the skin to remain adhered. Layers of retained skin can restrict the toes or tail, causing loss of these body parts.
Thinking of adding a fluffy, feathered, or scaled pet? Contact us with questions!







Leave A Comment